AMD Ryzen 6000 brings 6nm, RDNA 2, and Zen 3+ to laptops
AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series of laptop CPUs will bring a plethora of new features including a 6nm process, RDNA 2, Zen 3+ and more as it continues its assault on Intel’s laptop dominance. Here’s a comprehensive rundown of what’s coming from AMD:
- Enhanced TSMC 6nm process
- Up to 12 RDNA 2 compute units with hardware ray tracing support
- Double the integrated graphics performance of Ryzen 5000
- Up to eight cores capable of hitting 5GHz
- Up to 30 percent higher performance than Ryzen 5000
- Improved Zen 3+ cores
- PCIe 4.0
- DDR5 and LPDDR5 memory support
- Wi-Fi 6E
- Microsoft Pluton security processor support
- USB4
- Up to 24 hours of battery life
- Improved SmartShift Max mode
- Smart Access Graphics mode
- New Radeon RX 6800M and Radeon RX 6800S GPUs
Yup, that is indeed a plethora of features that AMD is conjuring in a lineup of no fewer than eight Ryzen H-class CPUs with core counts from 6 to 8, and three U-series chips you can gawk at below.
AMD
PCIe 4.0 at last! (for AMD)
AMD describes the new Ryzen 6000 series as a totally “new connected platform” and some of the features are badly overdue. AMD’s previous Ryzen 4000 and Ryzen 5000 series of CPUs largely outclassed Intel’s older 14nm 9th-gen and 10th-gen CPUs but had some deficiencies such as limited PCIe connectivity. Even though AMD was the first to PCIe 4.0 on desktops, it skipped the feature on its laptop chips and limited the CPU to just eight lanes of PCIe 3.0. With Ryzen 6000, AMD essentially doubles the Ryzen 5000’s GPU connection with support for eight lanes of PCIe 4.0. AMD has also wired in an additional 12 lanes to be used for storage and general plumbing.
USB4 finally
AMD laptops will support Wi-Fi 6E, which isn’t too hard, but AMD fans will surely applaud the arrival of USB4. The newest USB4 was announced officially on March 4, 2019 and it’s taken more than 1,000 days for it to show up on AMD’s laptops, which have always been at a disadvantage against Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 on Intel machines. In a nutshell, USB4 adopts and extends Thunderbolt 3 and can offer up to 40Gbps transfer speeds with devices as well as support for DisplayPort 2 and charging using USB-Power Delivery. Basically, for those who have been asking if a new AMD supports Thunderbolt 3 or not—you’ll no longer have to ask that question.

AMD
How much faster will Ryzen 6000 be?
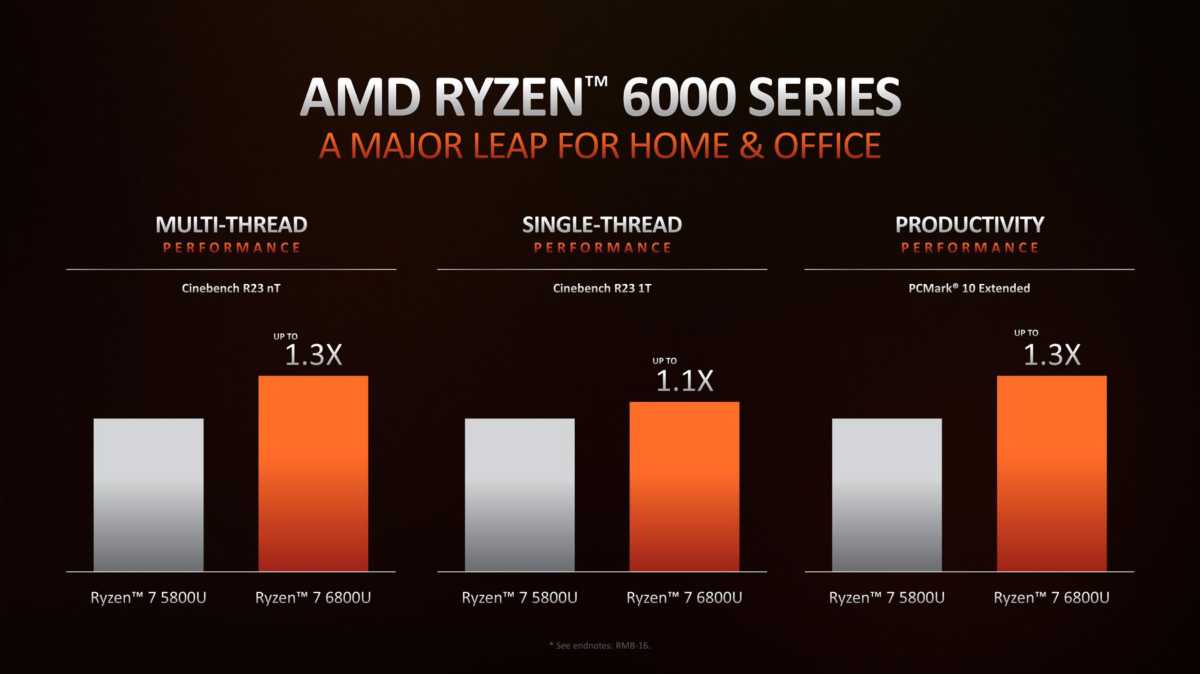
Core counts on the Ryzen 6000 CPUs don’t increase, so AMD banks on improvements in the manufacturing process and design to goose the chip over the existing Ryzen 5000 chips. According to AMD, it’s still a hefty bump, with the 8-core Ryzen 7 6800U offering a 30 percent increase in the CPU-focused Maxon Cinebench R23 benchmark in multi-threaded performance. Single-threaded performance is less impressive, but still a decent10 percent increase for the same chips. AMD said productivity will also see about a 30 percent increase using UL’s PCMark 10 Extended as its measuring stick.
Add the CPU core changes to the GPU core changes and you can get even more impressive performance, such as a 1.7x increase in Puget Systems Adobe Premiere Pro test and a 2.3x increase in Blender’s GPU Benchmark when comparing the Ryzen 7 6800U to a Ryzen 7 5800U.
Those RDNA 2 graphics cores in every Ryzen 6000 will also offer significant bumps in gaming with AMD saying a Ryzen 7 6800U will offer generally twice the 1080p gaming performance over its already pretty good Ryzen 7 5800U. AMD, in fact, says the new RDNA 2 cores in the Ryzen 6000 give it a 1.2x to 3x increase over Intel’s best Core i7-1165G7 Iris Xe graphics, as well as better performance than Nvidia’s GeForce MX450 GPU. While the newer graphics cores are largely responsible for the bump, some of the gaming performance also comes from the company’s full embrace of DDR5 and LPDDR5 RAM. Yes, the RAM that every person trying to build a desktop has been lighting up Reddit about.
AMD
Ryzen 6000 will only support DDR5; new Radeons
Although DDR5 on desktops has felt like it was introduced just to give those people whining about the lack of GPUs a “hold my beer” moment, AMD will skip DDR4 and LPDDR4X altogether and opt only for DDR5 at up to 4,800 mega transfers per second and LPDDR at up to 6,400 mega transfers per second. DDR5 and LPDDR5 offer decent bandwidth increases over DDR4 and LPDDR4X, and AMD plans to take advantage of that bandwidth for graphics.
It’s not only about integrated graphics, as AMD is also releasing new Radeon GPU as well under the Radeon RX 6800M and Radeon RX 6800S lineups. At the top end, the Radeon RX 6850M XT is expected to offer a moderate 7 percent boost over the previous RX 6800M GPU. You’ll see more performance on the Radeon RX 6650M XT and a non-XT version, which are expected to offer up to 20 percent more performance than the Radeon RX 6600M. At the lower-end, the Radeon RX 6500M and the Radeon RX 6300M will offer up to 200 percent more performance over a comparable Nvidia GeForce MX450, AMD said.
The Radeon RX 6800S is aimed at the fast-growing segment of sub-20mm gaming laptops that weigh less than 4.5 pounds. At the top end, the Radeon RX 6800S targets 100+ frame rates on max settings while the Radeon RX 6700S targets 100+ fps at high settings. A third entry, the Radeon RX 6600S, will target 80+ fps on high settings.
Welcome, Pluton
Security is increasingly important and closely wedded to the OS to be most effectiv. With Ryzen 6000, AMD will introduce the first PC CPU with Microsoft’s new Pluton security processor in its heart. Security is an entire book in itself, but Ryzen 6000 will support Shadow Stack, Memory Guard, and AMD Security Processor. You can read more about Microsoft Pluton here.
AMD
Optimized for power
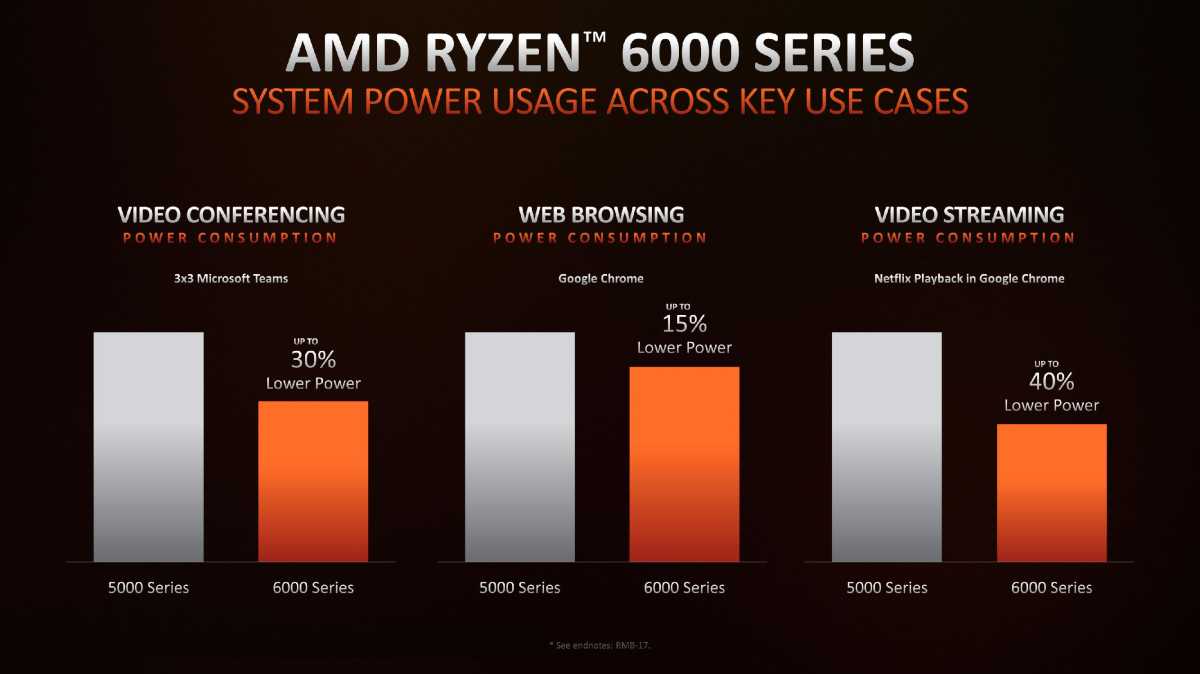
AMD has long prioritized power efficiency when running on battery and Ryzen 6000 continues with that philosophy. With Ryzen 6000, AMD is claiming 30 percent lower power used in a Microsoft Teams video conference, 15 percent better power consumption while browsing with Google Chrome, and 40 percent less power expended while watching a streamed Netflix movie in Chrome. AMD, in fact, said an OEM could build a laptop that can hit 24 hours of battery life playing a looped local video on a Ryzen 7 6800U laptop at 150 nits based on its internal tests.
200 laptops coming
The new Ryzen 6000 comes at a time when AMD has seen success in laptops that we frankly can’t ever recall the company having had before. Intel has long dominated laptops even more than desktops, but with the introduction of the Ryzen 4000 and Ryzen 5000, AMD finally cracked a segment that’s really just been gravy for the company. AMD said that success will continue this year with more than 200 premium laptops based on Ryzen 6000 coming. The company will also build on its burgeoning AMD Advantage program, with more than 20 laptops coming. AMD Advantage—a program that sets certain specifications on gaming laptops to improve the experience—also gets expanded with requirements for a minimum of a PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSD, 16GB of DDR5 RAM, new FreeSync Premium displays, and new “smart features.”
AMD
SmartShift Max, Smart Access Graphics
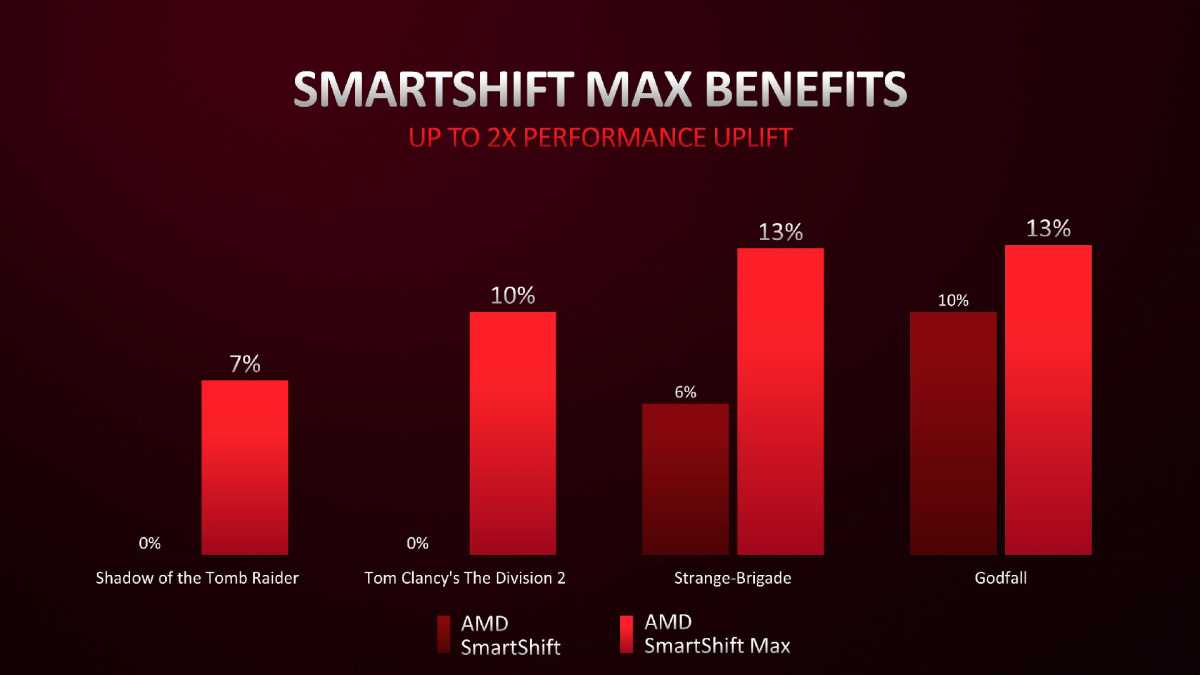
SmartShift Max is probably a familiar concept to many as it builds on the SmartShift feature that was introduced with the first AMD Advantage laptops. With SmartShift Max, the algorithms have been tweaked in how they shift power between the CPU and GPU and can offer up to a 2x increase in performance, AMD says. Much of the improvement comes from what the company learned with the original SmartShift, which tended to be a little aggressive in shifting power to the GPU.
With SmartShift Max, it’s now also aggressive about shifting power to the CPU, too. AMD officials said they’ve found that a surprising number of games that are less graphically intensive can benefit from pushing the CPU harder.
A new SmartShift Eco mode can actually detect when the laptop is running on battery and rather than running a game on the power-hungry discrete GPU, can instead dispatch it to the also-capable, albeit-slower integrated Radeon graphics in the Ryzen chip. The gamer can override the decision, but AMD officials said it can offer 2x the run time while playing on battery.
The last “smart” feature is called Smart Access Graphics is conceptually similar to Nvidia’s Optimus Advanced, which will automatically switch between running the discrete GPU directly to the screen for lower latency and slightly better performance and sending frames through the integrated graphics chip in hybrid graphics mode.

Right mouse click and select “open in new tab” to see original image. Ryzen 6000 will see use in more than 200 premium laptops this year
which is the most important win for AMD’s business.
AMD
One of founding fathers of hardcore tech reporting, Gordon has been covering PCs and components since 1998.
For all the latest Technology News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.
